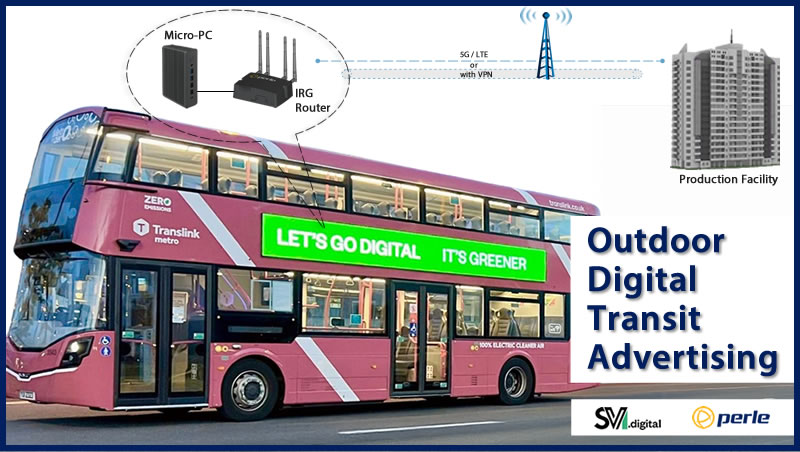
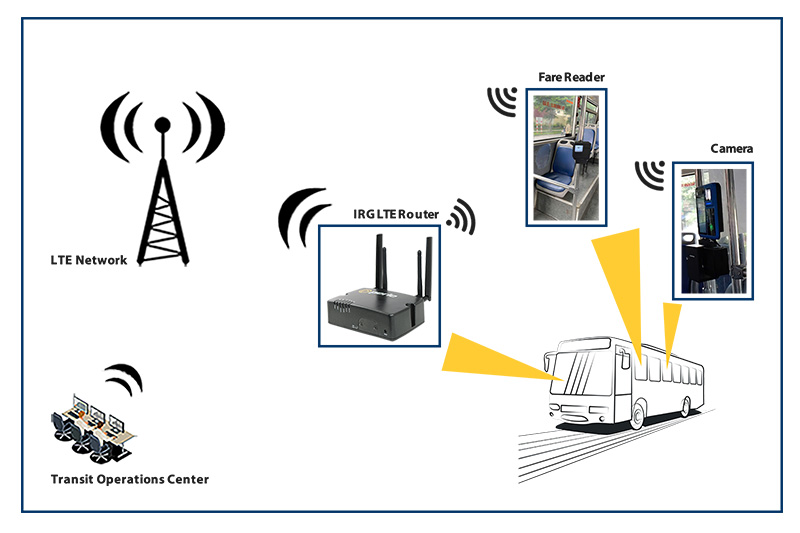
The intersection of data sets, science and storage
By Max BurkhalterFebruary 11, 2021
In an ever-changing global landscape, organizations are relying on data more heavily than in the past. To leverage data for the maximum positive effect, companies must increase their spending on data science. The global pandemic has produced new challenges across industries, and in some cases, dramatic budget cuts have been necessary to keep companies viable. According to experts quoted in a forecast by Datanami, significant investment in data science may make the difference between the survival of a business and forced liquidation.
The last mile in data science
Data powering machine learning applications can be compared to coding, as version control is difficult and outputs are based on probability rather than predetermination. Rapid build and deploy cycles are limited due to the fact that model training is processor-intensive. Substantial effort is needed to take machine learning operations, or MLOps, to new levels in the years to come. Increased demand for data scientists with experience using ML and AI will cause a shift in the employment market and an increased focus toward on-the-job learning as companies scramble to acquire and retain new talent.
However, enterprise customers can be expected to move away from building ML platforms. Instead, core competencies will include applying machine learning to business problems, leaving the building and maintenance of tools to third parties that provide software as a service. As Harvard Business Review reports, the challenges to last-mile data science implementation aren't technical, but organizational.
The intersection of data science and neuroscience offers several exciting possibilities, leading many to consider the futuristic implications for AI across industries. However, system and computational neuroscience and the interaction of both within the context of AI is still only in the early stages. The growth across both fields is heavily influenced by data visualization libraries. Server-side big data rendering, plotting libraries, more widely available power for computing and the reduced duplication of efforts is driving synchronization of neuroscience and AI.
Data sets
Critical business decisions are now being impacted by the results of analysis of large data sets, leading more organizations to hire chief data scientists whose focus is split between revenue generation through value creation, cost savings and risk management. Data scientists working for enterprises and SMBs are empowered by cloud computing, which now allows data to be processed, analyzed and leveraged for optimal results.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning both require and generate meaningful training data sets to make cause-and-effect correlations and to identify patterns. SaaS-based business applications will generate data primed to support more intelligent AI and machine learning. Data that is fed into ML algorithms can be leveraged to spot cause-and-effect relationships, but ever-changing data in new applications will require constant adaptation as systems learn to integrate such data into their DataOps ecosystem.

Data science
Formerly, primary data scientists were relegated to pre-production development and data sampling. While data engineers and machine learning engineers have slowly been added into the mix, their tasks are mostly linked to workflow scaling, production enhancement and code translation.
The data scientists of the future will be able to process data at a massive scale, reducing the need for such translation and shifting to a more active role within organizations. Data analysts can be upskilled and a competent data scientists in line with digital transformation as companies shift their approach to be focused on new tools and technologies.
The emerging role of the data scientist is powered by on-the-job training, reducing the need for a return to an institutional learning environment. As technology evolves and adoption rates grow, data scientists can be created, upskilled, re-skilled and working in advanced roles within mere months of hiring. Employees with internet technology or engineering degrees can be specifically prepared for these positions within the organization.
Data storage
Previously one of the most expensive aspects for SMBs and enterprises, data storage has increased in value but dropped in cost. Data warehouses and data lakes are being converted, stored in the cloud, accessed remotely and leveraged for business decision-making at all levels. They deliver actionable results as data is sorted, analyzed, micro-segmented and associated with KPIs for individual companies.
Meta tagging of images, visual recognition and personalized experiences on a consumer level is allowing data to be contextualized and converted from an unstructured format to a structured one. Metadata curation indicates that the value of metadata may soon exceed that of raw data itself. Serverless technology makes it easier to develop and deploy code, and computation power to crunch data becomes less costly and easier to access.
Today, the average company still depends on on-premise or hybrid solutions when it comes to serving the needs of their data scientists. Server support is of the utmost importance for companies, which requires industrial-grade server equipment to maintain constant operational efficiency. Perle delivers the high quality solutions your company needs to support databanks for your data scientists as the future of cloud computing continues to expand. Read our customer success stories to learn more.