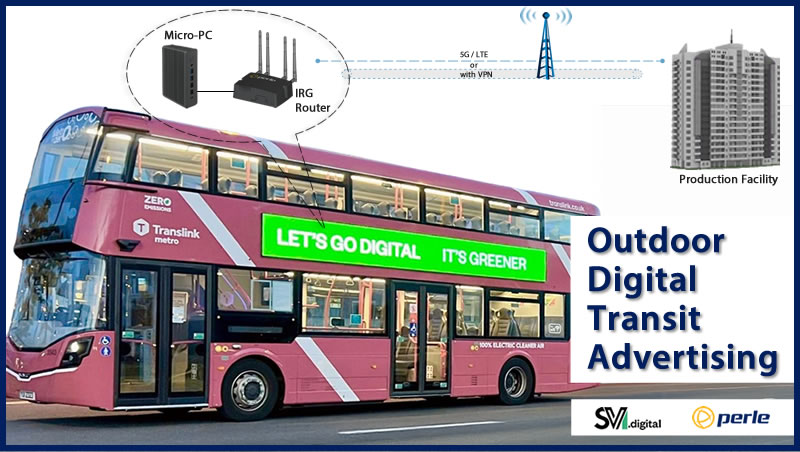
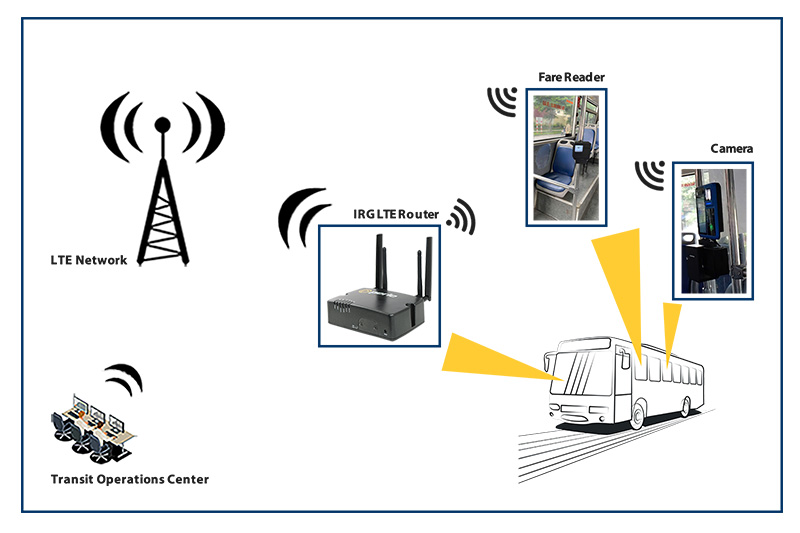
Risk: Why utilities need smart grid
By Max BurkhalterOctober 25, 2012
If you talk to some utility providers about the idea of making a heavy investment in smart grid technology and the subsequent networking solutions, you'll hear a lot about how they don't want to deal with the risk. The reasoning behind this is simple. When traditional networking tools interact with utility infrastructure, the system is vulnerable to all of the security threats facing both consumers and businesses.
Evaluating smart grid risk
Perhaps more importantly, utility providers understand that their infrastructure is absolutely critical to customers. If you were a utility provider, would you be rushing to tear down a tried-and-true service model to replace it with a new technology? Any innovative IT system presents inherent risks when being installed and developed, if only because it is new to the people using it, taking that initial plunge into the new system. Combined with the data protection issues associated with smart grid, the outlook can be grim in the eyes of pessimistic, and financially limited, utility providers.
A recent Electric Light & Power report explained that while many utility providers are aware of the risk associated with smart grid, they also realize that if they do not engage with the technology soon, they could fall behind.
How smart grid reverses risk
The data security issue is still being dealt with, primarily with new standards from industry and government bodies. The other major risk - transitioning from existing systems to the smart grid - requires a different vision from utility providers. The news source explained that the risk of replacing critical infrastructure with new systems is abated by the simple fact that smart grid is inherently more reliable than traditional utility systems.
According to the report, the evolving nature of utility infrastructure is such that organizations need to support bi-directional and multi-directional data transmission throughout the network. Traditional utility architectures would limit this functionality. Smart grid technologies are able to elevate the performance of the power distribution system to such an extent that it becomes more reliable, despite the inherent risks of putting new technology into practice.
Serial to Ethernet systems can help with this process, as the technology makes it much easier to integrate traditional networking components with specialized utility technology. This solution allows providers to cost-effectively establish Ethernet systems within the power distribution system, accelerating smart grid deployment.
Perle offers a range of cost effective serial-to-Ethernet converters to help meet NERC-CIP compliance for the protection of critical cyberassets in substations. The IOLAN SDS HV/LDC Terminal Server is designed to meet harsh environments associated with Power Substations with attributes such as support for substation AC and DC voltage ranges, extended operating temperatures and meeting emission, immunity and safety approvals associated with substation IT equipment.