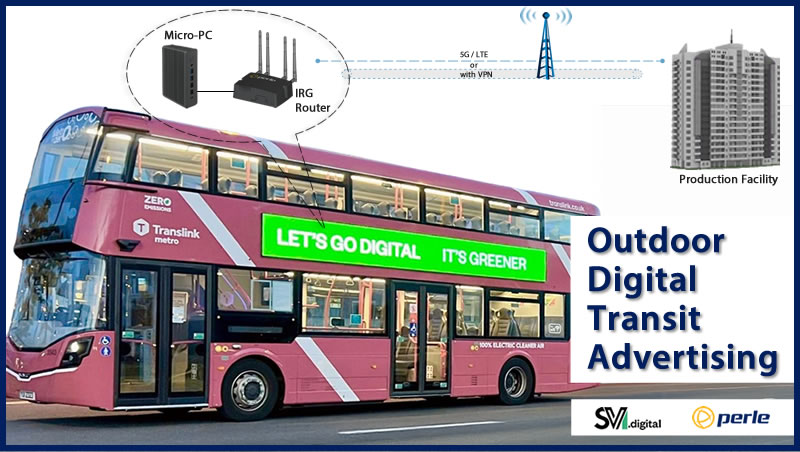
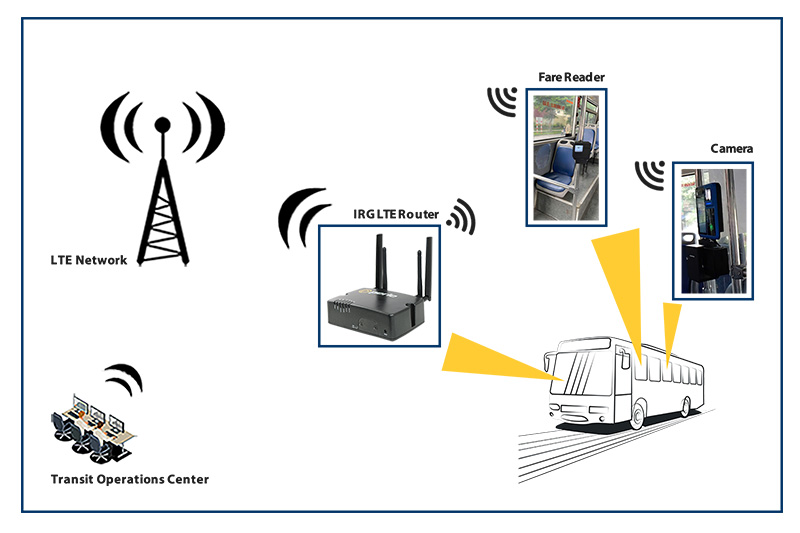
Smart grid deployments climbed substantially in 2011
By Max BurkhalterJanuary 27, 2012
The past year witnessed a significant rise in the number of smart grid solutions installed throughout the world. A recent survey of utility organizations from Microsoft and Osisoft found that the number of smart grid deployments climbed 25 percent during the past year. Furthermore, 28 percent of the company's involved in the survey are planning a move to smart grid, while just 24 percent said they currently have no strategies in place for the innovative technology.
Throughout the industry as a whole, smart grid is becoming a much more popular solution, as traditional utility systems have rapidly become outdated, difficult to manage and expensive to maintain. Because of this, approximately 63 percent of respondents to the survey said they are planning to increase their smart grid budgets during the next two or three years.
While many organizations in the utility sector are planning on sending money toward smart grid, there is also a significant tendency among providers to be uncertain as to how they should move forward. Smart grid involves a complex interplay of networking, monitoring and advanced utility technologies that must be supported by sophisticated security solutions. Because of this, 20 percent of those polled in the study said their move to smart grid has been slowed by technical issues.
Jon Arnold, managing director for the worldwide power and utilities industry at Microsoft and a member of the Smart Grid Advisory Committee to the National Institute of Standards and Technology, said that utility departments are increasingly facing a challenging decision between supporting innovation and taking technological risks.
"This year's survey shows that more and more utilities companies are adding new devices to the grid and incorporating new data sets into their operational capabilities. However, many of these same organizations are encountering significant interoperability and integration challenges. Leveraging technology and architectures that are adaptable removes many of the technology risks," said Arnold.
While smart grid is just beginning to take hold among most utility providers, the technology offers a revolution in the sector. Much of the power infrastructure around the world follows models that are incredibly outdated, leading to more outages and inefficient electricity distribution because of a lack of control over the system. Smart grid uses advanced networking technologies to create a more controllable utility environment that can reduce costs, limit outages and conserve electricity.
Perle offers a range of cost effective serial-to-Ethernet converters to help meet NERC-CIP compliance for the protection of critical cyberassets in substations. The IOLAN SDS HV/LDC Terminal Server is designed to meet harsh environments associated with Power Substations with attributes such as support for substation AC and DC voltage ranges, extended operating temperatures and meeting emission, immunity and safety approvals associated with substation IT equipment.