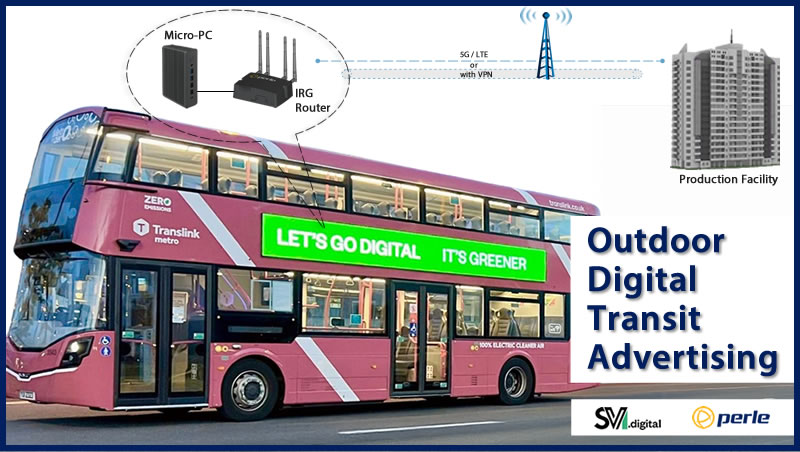
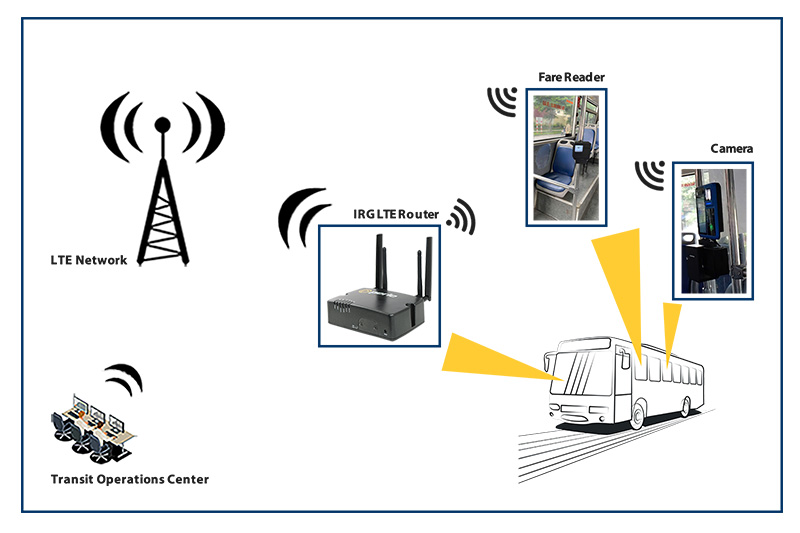
Smart grid security advances becoming critical
By Max BurkhalterFebruary 28, 2012
The smart grid is literally a revolution in how utility providers deliver power to homes and businesses. According to a recent SC Magazine report, the technology represents the most significant update to utility infrastructure in the past century. At the same time, it also consists of a major shift in the operational and environmental capabilities of power distribution systems.
According to the news source, this major shift in utility architectures brings change by connecting smart meters and other systems to a digital network. This allows individuals and utility providers to more carefully track electricity use, identify areas where efficiency gains can be made and improve the sustainability of the entire electric grid.
These substantial gains are driving utility innovation. At the same time, they are creating risks. The report said approximately 100 billion smart meters, sensors and other smart grid components will be deployed globally during the next five to ten years. Each of these individual devices will be connected to the internet, creating a major security risk within a utility system that is in dire need of innovation.
Because smart grid infrastructure is based on IP connectivity, they are faced with substantial cybersecurity risks that utility providers cannot take lightly. The news source explained that advanced malware systems, such as Stuxnet, can infect smart grid infrastructure and have a major impact on the utility grid, potentially sabotaging equipment. Because of this, organizations need to install multiple layers of security over the smart grid setup and ensure the network infrastructure is protected from even the most sophisticated threats.
SC Magazine explained that smart grid introduces personal data-related risks, as smart meters can transmit information about individuals and buildings that are extremely valuable. The technology also presents authentication problems. Unauthorized smart grids can swamp the utility provider with inaccurate and potentially harmful data that can compromise infrastructure settings.
The challenges of smart grid are clear, but so are the benefits. The utility gird has seen few major upgrades in the past 100 years, and the emerging technology completely updates the infrastructure to meet current power demands. This is especially prevalent as electronic vehicles, building automation and other similar products become more common. Smart grid is instrumental is supporting these initiatives by enabling more advanced power distribution that helps providers plan for usage spikes and deal with outages more effectively.
Perle offers a range of cost effective serial-to-Ethernet converters to help meet NERC-CIP compliance for the protection of critical cyberassets in substations. The IOLAN SDS HV/LDC Terminal Server is designed to meet harsh environments associated with Power Substations with attributes such as support for substation AC and DC voltage ranges, extended operating temperatures and meeting emission, immunity and safety approvals associated with substation IT equipment.