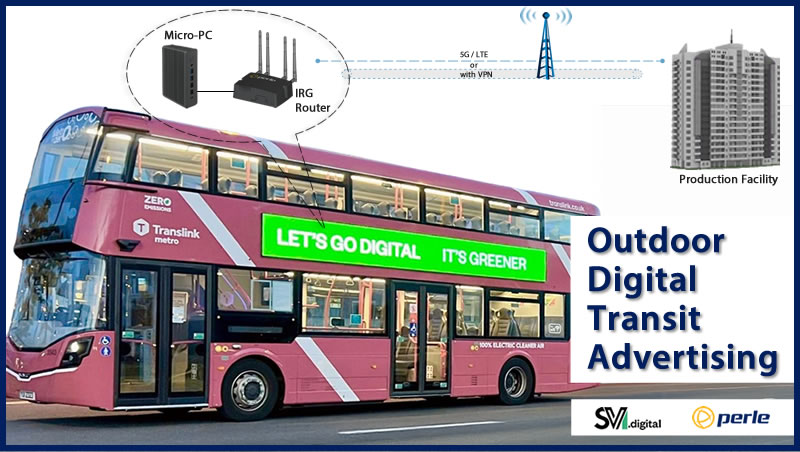
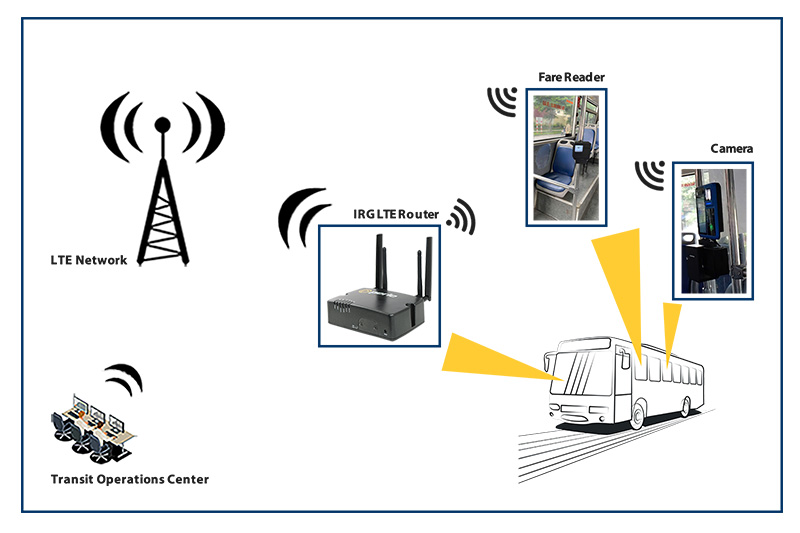
Smart meters not the focal point of energy innovation
By Donna DonnawitzNovember 29, 2012
If you look at smart grid news and studies over the past couple of years, one of the clearest areas of innovation on display is in smart meter technology. In theory, this represents a major strategic advance because metering solutions present a foundation upon which utility companies can build more efficient and sustainable energy distribution systems. However, a closer look at the current utility landscape reveals that smart meters are among the less important elements of the broad smart grid and significant resources have been wasted trying to widely deploy the technology, a recent study from the National Institute for Science, Law and Public Policy found.
The smart meter problem
Smart meters themselves are not a bad thing and the study does not declaim their role as a part of the broad smart grid infrastructure. However, the perceived role of smart meters is different than the actual part they play.
As a result, the large amount of state, federal and local government funding that has been pushed into smart meter deployment has been largely wasted because it would have been better used to solidify other parts of the smart grid. According to the study, many leaders had been led to believe that the core efficiency and financial gains offered by the smart grid would be realized, at least to some degree, by implementing smart meters on a large scale. The reality has been that the core utility distribution upgrades brought on by smart grid technologies are central to bringing about cost and sustainability gains, while smart meters play a secondary role.
Furthermore, the benefits of smart grid are limited by lack of consumer understanding and ability to use the technology. Jim Turner, chairman of the National Institute for Science, Law and Public Policy, explained that consumer-focused functionality will play a key role in the smart grid's future.
"A key element in a successful transition to a renewable energy economy will be establishing a clear 'demarcation' line between monopoly utility space and customer premises space, where the home gateway belongs to the consumer, not the utility," said Turner.
One technology that can fuel smart grid innovation in the core utility setup is serial to Ethernet media conversion tools. The solutions enable the foundational utility systems that use a limited serial network connection to communicate with Ethernet systems, allowing for better interoperability within the system.
Perle offers a range of cost effective serial-to-Ethernet converters to help meet NERC-CIP compliance for the protection of critical cyberassets in substations. The IOLAN SDS HV/LDC Terminal Server is designed to meet harsh environments associated with Power Substations with attributes such as support for substation AC and DC voltage ranges, extended operating temperatures and meeting emission, immunity and safety approvals associated with substation IT equipment.